

Hiring Dot NET developers matters most when organisations rely on business-critical systems, financial services, logistics platforms, healthcare workflows, or internal enterprise tools, that require reliability, security, and long-term continuity. Skilled .NET engineers ensure these platforms scale and evolve without introducing instability. Effective .NET talent sourcing demands far more than simply posting on job boards and scheduling interviews. It requires deep technical sourcing expertise, architecture fluency, and process rigour to ensure candidates thrive in high-stakes engineering environments.
The urgency of this specialisation is clear. As remote and hybrid work have become the norm, companies are now competing for the same global .NET talent pool rather than hiring from local markets.
According to the Stack Overflow 2024 Developer Survey, 38% of professional developers report working fully remotely, and a further 42% operate in a hybrid model, meaning 80% of the talent pool now expects geography-flexible roles.
When it comes to the .NET ecosystem: in the JetBrains report, 56% of C#/.NET developers say they use ASP.NET Core, a modern, cross-platform web framework for building high-performance APIs and cloud-ready backend services. This indicates that most of the ecosystem has shifted toward modern .NET development. For hiring teams, this means demand is highest for engineers experienced with ASP.NET Core rather than legacy .NET Framework stacks, increasing competition for candidates with up-to-date skills. While ASP.NET Core adoption is high, effective hiring goes beyond framework usage. The most valuable .NET engineers are those who can incrementally modernise legacy monoliths, often using approaches such as the Strangler Fig pattern, without destabilising business-critical systems.
As organisational reliance on distributed and hybrid engineering teams grows, precision in selecting the right .NET developer becomes ever more critical, not just for technical fit but for long-term retention and architecture success.
At DevsData LLC, we’ve built a tailored recruitment system that balances broad reach with selective quality, aligning specialised .NET engineers with enterprise-grade workloads. In this article, we share our methodology, real-world lessons and actionable insights to help you build a high-performance .NET engineering capability, without the hiring headache.
Dot NET development refers to building software using Microsoft’s .NET platform, a secure, high-performance ecosystem used across industries for web applications, backend services, cloud-native systems, desktop apps, and even mobile or IoT solutions. The platform supports multiple languages, most notably C#, and runs across Windows, Linux, macOS, and major cloud providers. Compared with alternatives such as Java (Spring) and Node.js, .NET is typically chosen for enterprise-grade systems where performance, security, long-term support, and tight cloud integration are critical.
| Area | .NET | Java (Spring) | Node.js |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Large, stable enterprise systems | Big enterprise applications | Fast, lightweight services |
| Performance model | Compiled, multi-threaded | JVM-based, multi-threaded | Event-driven, mostly single-threaded |
| Typical trade-off | Heavier enterprise stack | More configuration | Less suited for complex enterprise systems |
For clarity: .NET Framework is the legacy, Windows-only platform; .NET Core introduced cross-platform, open-source development; and modern .NET (versions 5+) is the unified successor that now drives most new development.
Modern .NET work is centred on .NET 6/7/8 and ASP.NET Core, which enable developers to create scalable, modular, and container-ready applications. Thanks to extensive libraries, robust tooling in Visual Studio and JetBrains Rider, and deep integration with Azure, .NET remains a preferred choice for organisations requiring stability, long-term maintainability, and enterprise-grade security.
Companies often select .NET for projects that demand reliability, performance, and strict compliance, such as financial platforms, healthcare systems, logistics infrastructure, and mission-critical internal tools.
As a result, Dot NET development has become a cornerstone of many enterprise technology stacks, driving continuous demand for experienced engineers who understand architecture, cloud environments, and modern development practices.
Hiring outcomes in .NET roles often suffer when seniority is inferred from titles rather than demonstrated capability. A clearer distinction emerges when candidates are evaluated across architecture, production readiness, and long-term ownership rather than years of experience alone.
Junior .NET developers typically demonstrate solid C# fundamentals and can contribute effectively within established ASP.NET Core codebases. They work well when requirements and architecture are clearly defined but rely on guidance for deeper framework behaviour, performance considerations, and structural decisions. Their experience is usually limited to operating within existing systems rather than shaping them.
Senior .NET developers, by contrast, are expected to design and evolve backend systems end to end. They understand .NET runtime behaviour, asynchronous execution, and framework internals, and they make informed architectural choices around scalability, reliability, and maintainability. Beyond feature delivery, they take responsibility for system health, performance, and long-term technical direction. In more mature organisations, senior .NET developers are also expected to collaborate with platform teams, understand infrastructure-as-code layers (such as Bicep or Terraform), and operate within service-mesh-enabled environments, even if they are not the primary owners of those platforms.
The difference becomes more pronounced in cloud and production environments. Junior developers can deploy through established CI/CD pipelines and work with cloud platforms at a basic level, while senior developers understand how .NET applications behave in containerised and distributed systems and can diagnose complex production issues. They anticipate failure modes, manage technical debt, and balance legacy stability with modernisation.
Security, compliance, and ownership further separate senior profiles. Junior developers generally follow prescribed security practices, whereas senior developers design systems with security and compliance in mind, communicate trade-offs to stakeholders, and mentor others. In environments with legacy .NET systems or regulated data, this depth of experience is often the deciding factor between short-term progress and sustainable delivery.
Using a structured skills matrix helps organisations align expectations, compensation, and responsibility, reducing the risk of mis-hires and ensuring that “senior” .NET developers bring real architectural and operational maturity, not just surface-level familiarity with the stack.
Because .NET Developer titles are not consistently tracked across countries, the most reliable way to size compensation is to triangulate official occupation wage data, global developer reporting, and region-level benchmarks (UK/EU). Together, these sources give a realistic range by seniority and location.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that Software Developers had a median annual wage of $133080 (May 2024), with the 10th percentile at $79,850 and the 90th percentile at $211,450, a practical seniority proxy (junior to senior/staff). BLS also publishes geographic wage/employment profiles (state/metro) for Software Developers, which can help when calibrating offers by region.
Stack Overflow’s 2024 Developer Survey shows the median annual salary for C# users is ~$65k (USD), which is useful as a cross-country anchor when comparing distributed talent pools. The same survey reports median Backend Developer compensation (USD) for major regions often used in remote hiring:
Backend roles are a strong proxy for many .NET positions, especially ASP.NET Core + services.
Hiring Dot NET developers offers organisations a reliable path to building secure, scalable, and long-lasting software systems. The .NET ecosystem continues to evolve rapidly, supported by strong community adoption, Microsoft’s long-term commitment, and proven performance across cloud, web, and enterprise environments. Below, we break down the key advantages companies gain by investing in experienced .NET talent, supported by a mix of industry reports, ecosystem surveys, and widely referenced benchmarks.
Modern .NET is one of the most actively used development platforms worldwide, giving companies a large, reliable, and continuously growing talent pool. According to the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, 27.1% of all professional developers reported using .NET in the past year, placing it among the top frameworks globally for professional engineering work.
This adoption stability means organisations benefit from predictable hiring, easier team expansion, and a lower risk of technology obsolescence, crucial for long-term enterprise systems and regulated-industry architectures.
.NET remains a preferred choice for companies operating high-scale, security-sensitive systems, including finance, healthcare, logistics, and government platforms. In its 2023 analysis, InfoWorld reported that .NET 7 showed big improvements in speed and efficiency for cloud and web tasks, which are important benefits for essential systems.
These improvements mean that hiring experienced .NET engineers directly contributes to better system performance, lower infrastructure cost, and more secure application foundations.
Since evolving into a fully open-source, cross-platform framework, .NET has become tightly aligned with modern cloud-native development practices. Its runtime is optimised for performance across Windows, Linux, and macOS, and it integrates seamlessly with containerisation tools such as Docker and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes.
This flexibility allows companies to build distributed backend services, modernise legacy systems, and deploy workloads consistently across Azure, AWS, and on-premise environments. Hiring experienced Dot NET developers ensures that cloud migrations, microservices architectures, and DevOps pipelines are executed efficiently, reducing friction and enabling faster, safer releases across multiple platforms.
A major reason companies hire .NET developers is the framework’s multi-decade continuity and Microsoft-backed roadmaps. A study published on arXiv, analysing long-term technology usage patterns, found C# and .NET show one of the highest “usage spans” in modern programming ecosystems, meaning developers tend to stay with these technologies for many years rather than switching frequently. In practice, this results in more stable hiring pipelines, stronger long-term maintainability, and lower risk of sudden skill shortages.
This longevity reduces the risk of technology turnover, lowers training and migration costs, and ensures that systems built today remain maintainable five, ten, or even twenty years from now.
Because .NET remains widely recognised and actively taught, organisations benefit from strong, ongoing talent availability. The Stack Overflow 2024 Developer Survey shows that C# remains the 7th most popular programming language globally, used by 27.86% of all professional developers.
Taken together, these advantages show why .NET remains a cornerstone of enterprise technology strategies. High adoption rates, strong performance benchmarks, deep cloud compatibility, and long-term ecosystem stability all make .NET developers uniquely positioned to build reliable, future-proof systems. For organisations scaling mission-critical platforms, hiring skilled .NET engineers is not just a technical choice, it is a strategic investment in security, maintainability, and sustainable growth.
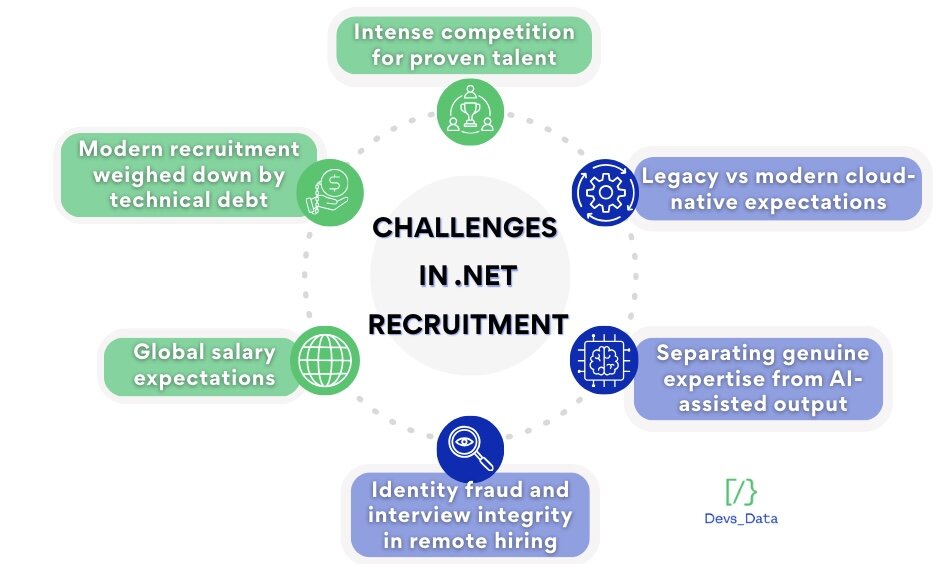
While Dot NET remains one of the most widely used and stable enterprise technologies, hiring truly skilled .NET engineers comes with challenges that are often underestimated. The global developer market is expanding, legacy systems create complex technical expectations, AI assistance obscures real skill levels, and remote-first hiring has introduced identity verification and compliance risks. Below, we break down the core obstacles organisations face, and how DevsData LLC systematically addresses each one.
The global developer market continues to expand, intensifying competition for truly senior .NET engineers rather than generalists with limited exposure. JetBrains estimates there will be 20.8 million professional developers worldwide in 2025, up from 18.2 million in 2023, increasing pressure on companies hiring experienced .NET talent.
As a result, .NET hiring is no longer local. Employers compete globally for engineers capable of owning complex distributed systems, performance-sensitive services, and secure platforms, skills that remain far rarer than basic .NET experience.
How we handle it at DevsData LLC
We treat .NET recruitment as a specialised discipline within a broad ecosystem, mapping talent by industry context, not just keywords. Our shortlists focus on engineers with proven end-to-end ownership of high-stakes systems, resulting in fewer but significantly more relevant senior candidates.
Many organisations must maintain legacy .NET Framework systems while moving toward modern .NET, cloud, and containerised architectures, creating a difficult hiring balance. Most candidates specialise in either legacy maintenance or modern cloud-native development, making engineers who can bridge both worlds far rarer than expected.
How we handle it at DevsData LLC
We clearly define the balance between legacy maintenance and modernisation for each role and assess candidates on both. This ensures expectations are aligned and hires match the real technical demands of the position.
The rapid adoption of AI coding tools makes it easier for weak candidates to mask their gaps during tests and interviews. InfoWorld reports that 85% of developers now use AI tools regularly for coding, and 62% already rely on at least one AI-powered coding assistant or code editor.
How we handle it at DevsData LLC
We design evaluations assuming AI assistance, combining time-boxed live sessions with deep discussions of real projects and design decisions. By focusing on system design, APIs, error handling, and migration strategies, we quickly distinguish genuine .NET expertise from AI-generated output.
Remote and hybrid hiring has opened the door to more sophisticated impersonation attempts, especially in IT roles. The Week reports that a March 2025 survey found around 17% of US hiring managers had already encountered candidates using deepfake technology in video interviews, with one executive noting that roughly 100 out of 827 applications for a software job were tied to fake identities.
How we handle it at DevsData LLC
We use multi-step identity verification, targeted technical screening, and reference checks to reduce impersonation risk. For sensitive .NET roles, we recommend staged system access until capabilities are proven.
As pay transparency laws expand, candidates are better informed, and often more demanding, around salary ranges for mid- and senior .NET roles. According to the 2025 US Pay Transparency Index by beqom, 12 US states plus six cities and counties already have some form of pay transparency law in effect, covering more than 60 million workers, with another 12 states preparing or implementing similar regulations.
How we handle it at DevsData LLC
We define role-specific compensation ranges based on stack complexity, sector, and geography, then validate them early against market feedback. This reduces late-stage offer risk and keeps packages competitive and realistic.
Many enterprises are still constrained by extensive legacy systems and technical debt, which directly shapes their .NET hiring needs. ITPro, citing research by Pegasystems and Savanta in 2025, reports that enterprises lose around $370 million per year on average to outdated legacy systems and technical debt, with 63% of IT leaders relying on between one and ten legacy applications daily and 29% using as many as twenty.
How we handle it at DevsData LLC
We are transparent about technical debt, modernisation plans, and time spent on legacy work, attracting .NET engineers aligned with the role’s real challenges and improving long-term retention.
Dot NET recruitment requires far more precision than simply screening for C# knowledge or ASP.NET experience. Market saturation, legacy-modernisation tension, AI-influenced assessments, identity fraud risks, pay-transparency pressures, and deep technical debt all complicate the hiring landscape. By approaching these challenges with structured verification, advanced technical evaluation, transparent expectation management, and industry-specific talent mapping, DevsData LLC helps clients secure .NET engineers who can genuinely deliver in complex, high-stakes environments.
Selecting a Dot NET recruitment partner is an important decision for organisations that depend on secure, long-lived backend systems. A strong .NET recruitment partner must do more than source resumes, they must understand the nuances of modern .NET versions, legacy migration pathways, cloud alignment, architectural patterns, and the realities of hiring for long-term maintainability.
Below are key criteria to help you evaluate whether an agency has the technical depth, precision, and process maturity to deliver high-calibre .NET engineers.
| Key area | What to look for | How to assess |
|---|---|---|
| Technical evaluation depth | A structured, architecture-aware .NET screening framework covering C#, ASP.NET Core, cloud workflows, debugging, performance tuning, and observability. | Ask the agency to walk you through its .NET evaluation rubric and request anonymized examples of modern .NET (6/7/8) and system design assessments. |
| Legacy and modernisation expertise | Ability to identify developers capable of working on both legacy .NET Framework systems and modern .NET Core / cloud-native solutions. | Request examples of placements in modernisation projects and how candidates are evaluated for both legacy remediation and greenfield development. |
| Cloud and DevOps alignment | Strong understanding of .NET integration with Azure, AWS, containers, CI/CD, and microservices. | Ask for anonymized case studies demonstrating how the agency assessed cloud readiness or container/microservices experience. |
| Security and reliability screening | Screening practices tailored to regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, logistics, and government. | Verify how secure coding, identity handling, auditing, and incident response experience are evaluated during the hiring process. |
| Proven track record with measurable results | Documented success in delivering .NET engineers with strong retention and client satisfaction metrics. | Request case studies showing time-to-hire, retention, seniority placed, performance feedback, and client references. |
| Global and regional talent knowledge | Clear understanding of .NET talent clusters, regional salary norms, and availability across markets. | Ask which markets they source from and how they adjust searches based on seniority, cloud expertise, or industry background. |
| Process transparency and communication quality | Predictable pipelines, expectation alignment, and visibility into every recruitment stage. | Ask for a sample hiring pipeline walkthrough, including communication checkpoints and candidate risk-management methods. |
Website: www.devsdata.com
Team size: ~60 employees
Founded: 2016
Headquarters: Brooklyn, NY, and Warsaw, Poland
DevsData LLC is a trusted partner in specialised Dot NET recruitment, with a strong track record of placing senior C#, ASP.NET Core, and cloud-native .NET engineers into complex, mission-critical environments across the US, Europe, and Israel. We focus on long-term architectural impact, matching organisations with developers who can stabilise legacy .NET systems, modernise infrastructure, and build scalable backend services that directly support business continuity and performance.
With a proprietary network of 65000+ vetted professionals and a 60+ person recruitment and consulting team, we combine AI-enhanced sourcing with architecture-aware technical interviews and rigorous system-design assessments. Every candidate passes through multi-stage, 90-minute technical reviews, behavioural evaluations, and cloud-readiness checks, resulting in a sub-6% acceptance rate. This ensures clients see only top-tier .NET engineers capable of working across .NET Framework, .NET 6/7/8, containerisation, and modern cloud ecosystems.
DevsData LLC operates under an official, government-approved European recruitment license and works on a success-fee model with a guarantee period for every placement. Our portfolio spans FinTech, Healthcare, Logistics, eCommerce, and Enterprise SaaS, with 100+ completed engagements for 80+ global clients and 5.0 ratings on platforms like Clutch and GoodFirms. We are recognised for precision, technical depth, and the ability to deliver .NET talent that strengthens platforms, accelerates delivery, and supports long-term scalability.
Hiring .NET experts for SportRadar AG

SportRadar AG, a global leader in sports analytics and betting technology, required highly specialised .NET experts to support large-scale data processing and complex backend systems. The challenge was precision: candidates needed deep knowledge of C#, ASP.NET, distributed systems, and high-throughput architectures capable of handling massive real-time workloads. Our approach combined architecture-focused interviews to assess system design and scalability, performance-scenario questions based on real-world constraints, and practical debugging simulations drawn from actual production issues. This allowed us to evaluate how candidates reason, diagnose problems, and operate under realistic conditions. This allowed us to identify engineers who could operate confidently in high-load, low-latency environments.
Key learning: for data-intensive and performance-driven .NET roles, evaluating architecture reasoning and production-readiness is as important as testing raw coding ability.
Recruiting engineers for Gyldendal Norsk Forlag

Gyldendal, one of Norway’s largest publishing groups, needed engineers capable of modernising internal systems while ensuring long-term stability of legacy applications. The complexity lay in bridging two worlds: candidates needed hands-on experience with modern .NET Core, cloud workflows, and microservices, while also being able to maintain older .NET Framework systems supporting editorial tools and content pipelines. We used a dual-track screening approach that evaluated both sides of the role. Candidates were assessed on how well they understand system migration, including moving from older .NET codebases to modern versions, as well as on their ability to design clean APIs and maintain code quality in legacy systems. At the same time, we examined whether they could introduce modern development practices gradually, without disrupting existing workflows or creating stability risks.
Key learning: when legacy and modern .NET coexist, the right hire is someone capable of incremental modernisation, not just greenfield development.
Building a distributed engineering team for Memcare

Memcare, a Nordic digital services platform, needed strong backend and full-stack engineers able to work across multiple regions and handle sensitive data with strict compliance requirements. The challenge was identifying candidates who combined .NET expertise with secure-by-design thinking, clear communication, and experience working in distributed remote teams. Many applicants had solid technical backgrounds but lacked the maturity required to work in high-trust, privacy-focused environments. We incorporated structured behavioral evaluation, secure-coding scenario interviews, and cross-functional problem discussions to uncover candidates with both technical rigor and reliability.
Key learning: in privacy and compliance-sensitive .NET roles, evaluating secure development habits and communication maturity is critical to long-term success.
Not sure whether your organisation truly needs a dedicated Dot NET Developer right now? Take this quick self-assessment. Answer the questions below and count how many times you answer “yes.”
Mostly yes: you’ll benefit from hiring a specialised Dot NET developer. The right engineer will stabilize your codebase, accelerate delivery, modernise legacy systems, and strengthen backend reliability, especially in cloud or high-scale environments.
Mostly no: your current team may be sufficiently equipped for now. Revisit this when you plan architecture changes, cloud migrations, refactoring cycles, or major product expansions that require deeper .NET expertise.
Dot NET recruitment is a domain that requires deep architectural understanding, rigorous technical evaluation, and the ability to differentiate between surface-level C# skills and true engineering competence. As organisations balance legacy codebases with modern cloud-native .NET applications, a mis-hire can slow delivery, amplify technical debt, and compromise the stability of mission-critical systems.
The reality is clear: .NET remains one of the most widely adopted and durable enterprise technologies, but not all developers who list it on their resume can navigate complex migration paths, performance-sensitive services, or secure backend architectures.
Evaluating candidates for system design ability, debugging maturity, cloud alignment, and long-term maintainability is now just as important as verifying their knowledge of C# syntax.
At DevsData LLC, we focus on what truly matters in Dot NET recruitment: architectural thinking, production-readiness, experience across both legacy and modern .NET, and the discipline to deliver stable, scalable backend systems. Our methodology combines AI-enhanced sourcing, multi-stage technical interviews, cloud-readiness assessments, and behavioural evaluation tailored to high-stakes engineering roles. With a vetted talent network of 65000+ professionals, 100+ completed projects, and clients across the US, Europe, and Israel, we deliver .NET hires who strengthen platforms, accelerate product development, and reduce long-term technical risk.
Whether you are modernising a legacy monolith, building a new .NET 8 microservices architecture, or scaling your engineering organisation, DevsData LLC provides precision, trust, and a measurable impact on technical performance.
Learn more at www.devsdata.com or contact general@devsdata.com.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
DevsData – your premium technology partner
DevsData is a boutique tech recruitment and software agency. Develop your software project with veteran engineers or scale up an in-house tech team of developers with relevant industry experience.
Free consultation with a software expert
🎧 Schedule a meeting
FEATURED IN


DevsData LLC is truly exceptional – their backend developers are some of the best I’ve ever worked with.”
Nicholas Johnson
Mentor at YC, serial entrepreneur
 Build your project with our veteran developers
Build your project with our veteran developers
 Explore the benefits of technology recruitment and tailor-made software
Explore the benefits of technology recruitment and tailor-made software
 Learn how to source skilled and experienced software developers
Learn how to source skilled and experienced software developers




Categories: Big data, data analytics | Software and technology | IT recruitment blog | IT in Poland | Content hub (blog)
